To be published in 《Shanghai City Planning》
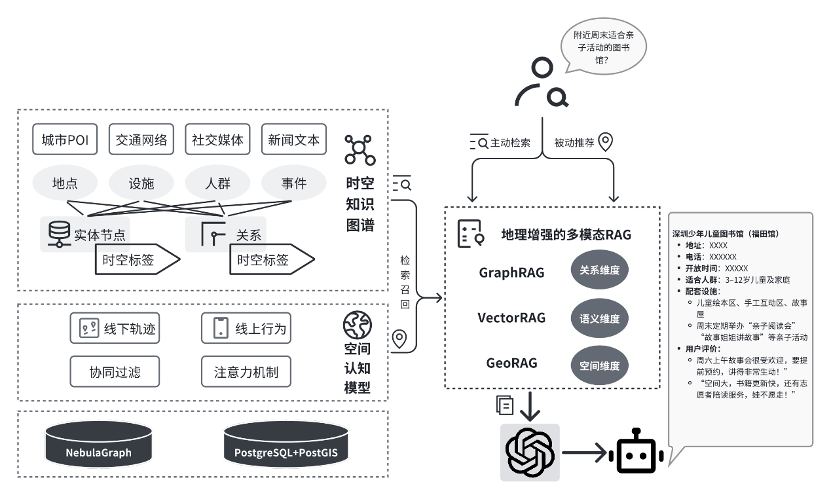
In the context of life circle planning and community governance, large language models (LLMs) can play a pivotal role in several key areas. Firstly, through natural language interaction, LLMs can understand residents' genuine needs in various contexts, automatically extracting demand themes and sentiment tendencies from chat records, survey texts, and social media comments. This enables automatic categorization and prioritization of demands, addressing the challenges of high heterogeneity in resident needs and unstructured expression methods, thus facilitating precise service provision. Secondly, LLMs can semantically integrate and model relationships among data from sensor networks, community GIS, demographic statistics, and government service platforms, enhancing the interpretability and operability of data. This supports functional assessment, resource allocation, and spatial optimization of life circles. Additionally, in the process of collaborative community governance, LLMs can act as "intermediary agents," facilitating semantic bridging between residents and diverse entities such as street offices, property management, and enterprises. They assist in policy interpretation, topic negotiation, consensus generation, and other processes, thereby improving collaboration efficiency and satisfaction.
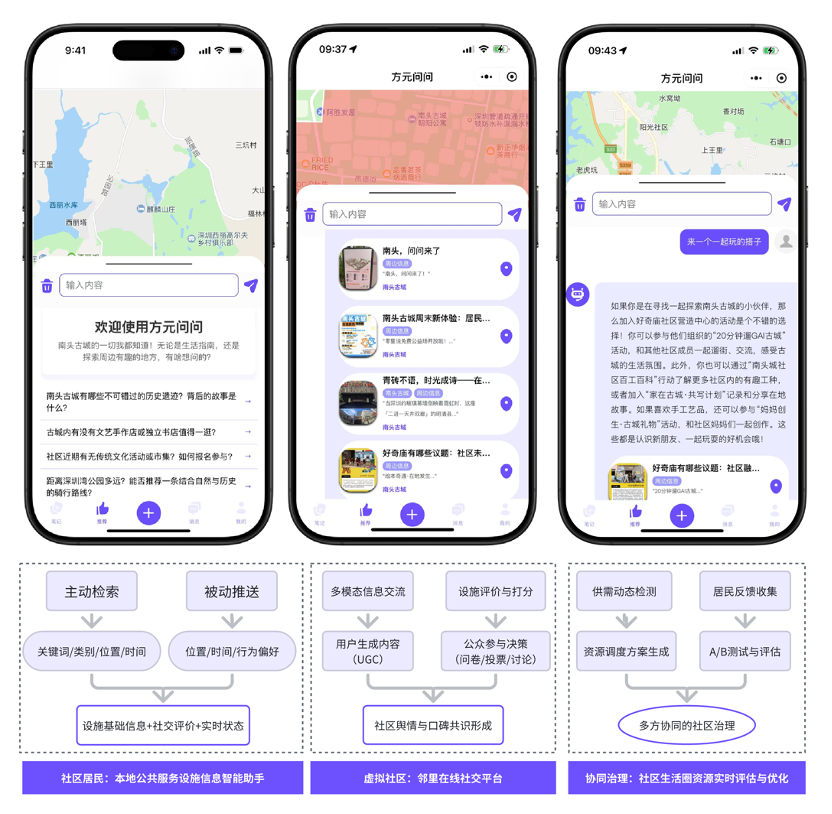
The WeChat mini-program "方元问问" (Fangyuan Wenwen), developed by our lab members Li Boyang and Huang Nuoxian, partially implements the scenarios of large model-assisted life circle planning and governance. It focuses on providing an intelligent assistant for public service facility information for community residents and businesses, and has been piloted in the Nantou Ancient City community in Shenzhen. This application utilizes natural language interaction through the WeChat mini-program, combined with community geographic information and multimodal data, to enable intelligent querying and recommendation of community public service facilities, providing residents with convenient service navigation and consultation. Additionally, it supports information sharing and transactions between community residents and businesses, aiding in the management and operation of public service facilities in the community.
📅 Release Date: August 26, 2024